Den som mätte upp området kring Nyen var emellertid en infödd svensk: Erich Nilsson Aspegreen. Han var en lantmätare som först lejts privat av Gustav II Adolfs halvbror Carl Carlsson Gyllenhielm. Denne hade på 1620-talet utnämnts till det svenska rikets förste ståthållare i Ingermanland. När det blev aktuellt med staden Nyens utvidgning, skedde detta bl.a. genom intrång på Gyllenhielms domäner.
Kart & Bildteknik 2003:3, artikel "Från Nyen till Hiddensee. Svensk kartläggning under 1600-talet". Av Ulla Ehrensvärd.
(1812–1879) was a British born American artist working in watercolor, gouache, lithography, and engraving.
Hill's work focussed primarily upon natural subjects including landscapes, still lifes, and ornithological and zoological subjects. In the 1850s, influenced by John Ruskin and Hill's association with American followers of the Pre-Raphaelite Brotherhood, his attention turned from technical illustration toward still life and landscape.
Hill was the son of British aquatint engraver John Hill. He emigrated with his parents from London to the United States in 1819, initially living in Philadelphia. In 1822 the family moved to New York, where Hill apprenticed in aquatint engraving in his father's shop.
In 1838 Hill married Catherine Smith - their children included the astronomer George William Hill and the painter John Henry Hill.
In watercolor and aquatint engravings, Hill employed a stipple technique, building up planes of softly gradated colors made of tiny brushstrokes–a process commonly seen in painted miniatures. Applied to a larger scale on canvas the result was a form of objective real...
Bland arbeten.
Encyclopédie ou dictionnaire universel raisonné des connaissances humaines.
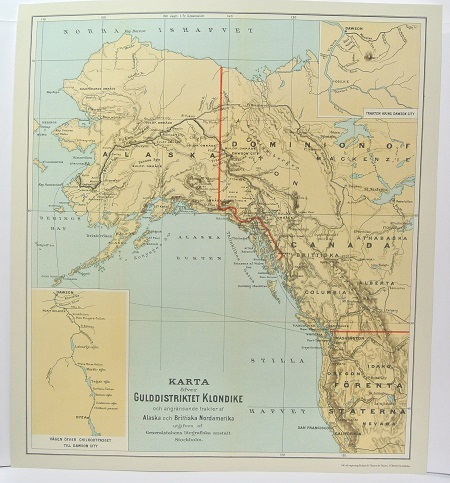
Gulddistriktet Klondike - ca 1897.
Blue Vases, Pl. XII
Olaus Magnus text till den berömda kartan "Carta Marina".
Texten finns även på katalanska, spanska och engelska.
Bureus karta över norden
Kartor och atlaser
Bilder och planschverk
Teckenförklaringar

Porträtt på Gerard Mercator och Jodocus Hondius.
"Striking image showing Mercator and Hondius in their idealized workshop.
This famous portrait of two of the most important mapmakers during the Golden Age of Dutch cartography was engraved by Coletta Hondius, as a tribute to her late husband, shortly after his death. Gerard Mercator is shown with his successor, Jodocus Hondius, seated at a table surrounded by the implements of their trade. The fine portrait is set within an elaborate strapwork framework that includes a wall map of Europe.
Gerard Mercator is renowned as the cartographer who created a world map representing new projections of sailing courses of constant bearing as straight lines—an innovation which, to this day, enhances the simplicity and safety of navigation. In his own day, Mercator was the world's most famous geographer. He created a number of wall maps early in his career, as well as one of the earliest modern world Atlases in 1595. Although this was the first appearance of the word Atlas in a geographical context, Mercator used it as a neologism for a treatise on the creation, history and description of the universe, not simply a collection of maps. He chose the word as a commemoration of King Atlas of Mauretania, whom he considered to be the first great geographer.
Jodocus Hondius was a Dutch engraver and cartographer. He is best known for his early maps of the New World and Europe and for continuing publication of Gerard Mercator's World Atlas. He also helped establish Amsterdam as the center of cartography in Europe in the 17th century. In England, Hondius publicized the work of Francis Drake, who had made a circumnavigation of the world in the late 1570s. In 1604, he purchased the plates of Gerard Mercator's Atlas from Mercator's grandson and continued publication of the Atlas, adding his own maps over the next several decades. Hondius later published a pocket version Atlas Minor."