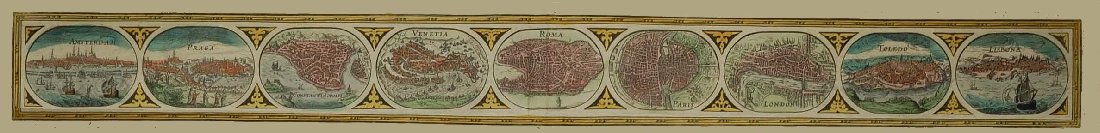
Född 1833 5/9 i Ljusdals sn (Gävleb.), död 1889 3/3 i Karlstad.
Major i armén. Landshövding. Kartograf och etsare. Son av lantmätaren och landshövdingen Per Henrik W. och Carolina Andrietta Ström. Kartograf vid Rikets allmänna kartverk 1859-73. Var kapten vid Hälsinge regemente och major i armén, då han 1873 utnämndes till landshövding i Norrbottens län. Erhöll 1885 transport till Värmlands län.
Bland arbeten.
Karta över Göta kanal med utsikter, efter A. Nay, etsn.
Hultmark, 1944.
ÖRNEHUFVUD, OLOF HANSSON SWART.
Född 1600 i jan. i Nya Lödöse, död 1644 27/8 i lägret vid Kattarps by i Västra Skrävlinge sn (Malm.).
Fortifikationsofficer. Kartograf. Tecknare och kopparstickare. Son av handlanden Hans Olofsson och Anna Eriksdotter. Student vid universitetet i Rostock. Skrivare i hertog Johans kanslo 1617 och i kungl. kansliet 1619-24. Fick 1624 Gustav II Adolfs befallning att öva sig i ritare- och ingenjöreskonsten under Anders Bures [Bureus] ledning. Utnämndes 1625 till 'geographus'. Blev 1628 konduktör och 1632 generalkvaratermästare vid Fortifikationen. Adlades 1635 med namned Örnehufvud. Kallade sig tidigare Olof Hansson, Olawus Johannis Gothus och Oluff Hansson Swart. 'Avtecknade såsom åsyna vittne de flesta svenska aktioner och belägringar under tyska kriget; avritade slutligen ävenledes en längd av rikets provinser, synnerligast de vid gränserna med alla dess skärgårdar och hamnar'.
Bland arbeten.
Rigas kapitulation 1621, kopparstick.
Elgenstierna.
Se GERRITSZ.
[Tooley]
Tooley.
Ingermanlandiae – Homanns Erben 1734
'Lemland' - Finland 1943.
Olaus Magnus text till den berömda kartan "Carta Marina".
Texten finns även på katalanska, spanska och engelska.
Bureus karta över norden
Kartor och atlaser
Bilder och planschverk
Teckenförklaringar

Porträtt på Gerard Mercator och Jodocus Hondius.
"Striking image showing Mercator and Hondius in their idealized workshop.
This famous portrait of two of the most important mapmakers during the Golden Age of Dutch cartography was engraved by Coletta Hondius, as a tribute to her late husband, shortly after his death. Gerard Mercator is shown with his successor, Jodocus Hondius, seated at a table surrounded by the implements of their trade. The fine portrait is set within an elaborate strapwork framework that includes a wall map of Europe.
Gerard Mercator is renowned as the cartographer who created a world map representing new projections of sailing courses of constant bearing as straight lines—an innovation which, to this day, enhances the simplicity and safety of navigation. In his own day, Mercator was the world's most famous geographer. He created a number of wall maps early in his career, as well as one of the earliest modern world Atlases in 1595. Although this was the first appearance of the word Atlas in a geographical context, Mercator used it as a neologism for a treatise on the creation, history and description of the universe, not simply a collection of maps. He chose the word as a commemoration of King Atlas of Mauretania, whom he considered to be the first great geographer.
Jodocus Hondius was a Dutch engraver and cartographer. He is best known for his early maps of the New World and Europe and for continuing publication of Gerard Mercator's World Atlas. He also helped establish Amsterdam as the center of cartography in Europe in the 17th century. In England, Hondius publicized the work of Francis Drake, who had made a circumnavigation of the world in the late 1570s. In 1604, he purchased the plates of Gerard Mercator's Atlas from Mercator's grandson and continued publication of the Atlas, adding his own maps over the next several decades. Hondius later published a pocket version Atlas Minor."