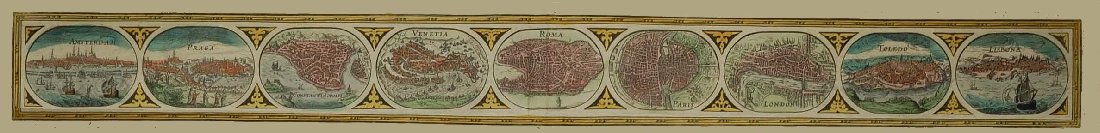
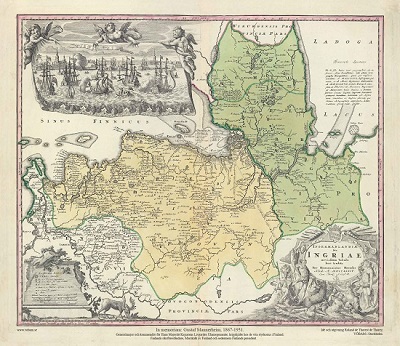
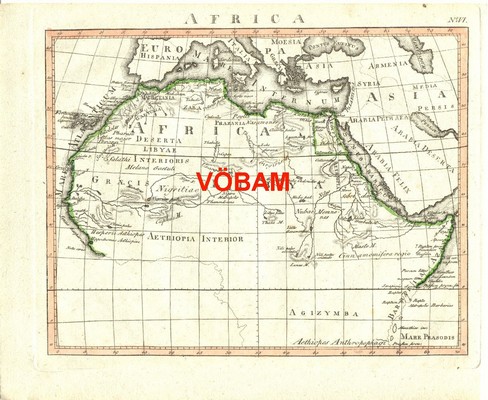
SANSON, NICOLAS.
Biografiska uppgifter:1600-67. Född i Abbevile, död i Paris.
Fransk geograf. Han fick en grundlig utbildning i klassiska språk, historia och geografi. Hans första arbete, 'Galliae antiquae descriptio geographica' utkom 1627 och följdes två år senare av en karta över det gamla Gallien i 6 delar. År 1627 fick han titeln Géographe du Roi (Ludvig XIII) och blev samtidigt ingenjör i provinsen Picardie. Sin första atlas gav han ut 1654 och den innehöll 100 kartor. 1658 kom en ny atlas med 113 kartor som hade titeln 'Cartes génerales de toutes les parties du monde'. Denna utgavs av bokhandlaren Pierre Mariette (se denne) som även ombesörjde en nyutgåva 1664, då utökad till 147 kartor. Av Sansons geografiska arbeten i övrigt kan nämnas 'Graeciae antiquae descriptio' (1636), 'Index geographicus' (1653) och 'Geographia sacra'. Sansons verksamhet var av grundlägande betydelse för utvecklingen av fransk geografi och han var en lärare för de yngre generationerna. Hans egna kartarbeten övertogs av sönerna Guillaume (se denne) och Adrien (se denne) , samt sonsonen Pierre Moulard Sanson (se denne).
Nicolas Sanson (1600–1667) was a French cartographer, wrongly termed by some the creator of French geography. He was born of an old Picardy family of Scottish descent, at Abbeville, on the 20th (or 31st) of December 1600, and was educated by the Jesuits at Amiens.
In 1627 he attracted the attention of Richelieu by a map of Gaul which he had constructed (or at least begun) while only eighteen. He gave lessons in geography both to Louis XIII and to Louis XIV; and when Louis XIII, it is said, came to Abbeville, he preferred to be the guest of Sanson (then employed on the fortifications), instead of occupying the lodgings provided by the town. At the conclusion of this visit the king made Sanson a councillor of state.
Active from 1627, Sanson issued his first map of importance, the 'Postes de France', which was published by Melchior Tavernier in 1632. After publishing several general atlases himself he became the associate of Pierre Mariette, a publisher of prints.
In 1647 Sanson accused the Jesuit Philippe Labbe of plagiarizing him in his Pharus Galliae Antiquae; in 1648 he lost his eldest son Nicolas, killed during the Fronde. Among the friends of his later years was the great Condé. He died in Paris on 7 July 1667. Two younger sons, Adrien (d. 1708) and Guillaume (d. 1703), succeeded him as geographers to the king.
In 1692 Hubert Jaillot collected Sanson's maps in an Atlas nouveau. See also the 18th century editions of some of Sanson's works on Delamarche under the titles of Atlas de géographie ancienne and Atlas britannique; and the Catalogue des cartes et livres de géographie de Sanson (1702).
Bland arbeten:
Sanson's principal works are:
Galilee antiquae descriptio geographica (1627);
Graeciae antiquae descriptio (1636);
L'Empire romain (1637);
Britannia, ou recherches de l'antiquité d'Abbeville (1638), in which he seeks to identify Strabo's Britannia with Abbeville;
La France (1644);
Tables méthodiques pour les divisions des Gaules (1644);
L'Angleterre, l'Espagne, l'Italie et l'Allemagne (1644);
Le Cours du Rhin (1646);
In Pharum Galliae antiquae Philippi L'Abbe disquisitiones (1647-1648);
Remarques sur la carte de l'ancienne Gaule de César (1651);
L'Asie (1652);
Index geographicus (1653);
Les Estats de la Couronne d'Arragon en Espagne (1653);
Geographia sacra (1653);
L'Afrique (1656)
Sanson, Nicolas (1656), Le Canada ou Nouvelle France, &c., Paris: Chez Pierre Mariette, OCLC 32881783
Sanson, Nicolas (1658), Cartes générales de toutes les parties du monde, Paris: P. Mariette, OCLC 11510414
Cartes génerales de toutes les parties du monde.
(Nouv. biogr. gen. - Tooley.)
Tillbaka till början.