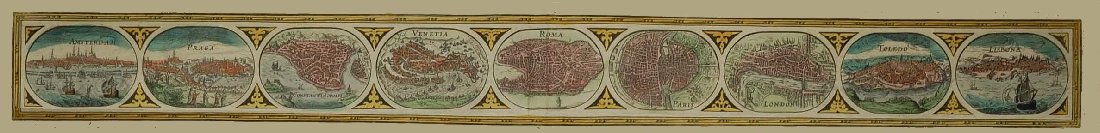
fl 1610-1635.
Nicolaes van Geelkercken, one of the lesser-known figures of the highly productive Dutch period at the beginning of the seventeenth century, was active as an engraver, cartographer and publisher in Leiden, Amsterdam and Arnhem. He was later become the Surveyor of Gelderland.
His earliest known work is a world map of 1610. His second world map published by Janssonius in Amsterdam, in the second state with the addition of Le Maire’s Strait.
Engraver, cartographer, publisher active in Leyden, Amhem and Amsterdam in the early years of the seventeenth century. His maps, though few in number, were particularly elegant.
Bland arbeten.
World map 1610 / 1618.
Sotheby's
Ca 1665-1749. Föddes ca 1665 i Vimmerby och dog samt begravdes 1749 i Djursdala, Orremåla.
Kronolänsman i Sevede, 'År 1998 gav han (Owe Gustavs) ut i Rostock en mycket vacker skrift Schwedische Landesaufnahme 1692-1709. Hiddensee 1695 (ISBN 3-9806246-0-9). I denna reproduceras den 2 meter långa kartan (i skala c. 1:8.100) med beskrivande text. Kartan ritades av Olof Spaak, som tillhörde Gunno Eurelius värmländska skara'.
'Framvistes för rätten Länsmannens Olof Spaaks skrifteliga bevittnade förordnande under den 27 nästlidne martü, heremedelst han förklarar sin vilja vara att dess yngsta barn, Olof, Lars, Hans och Annicka, skola efter hans död vara lika arvtagare i löst och fast, samt att de öfrige hans barn, icke den ringaste utalan derå göra skola eller något af hans efterlemnade egendom hafva att fordra, som anteknades åliggandes förenämnde som testamentet fått enligt lag det å nyo efter givarens död för rätten uppvisa, och tillika en riktig afskrift deraf ingifva.'
(E VII aac 1749 volym 111. - Utdrag ur Sevedes Härads ting den 19 Maj 1749.)
Kart & Bildteknik 2003:3, artikel "Från Nyen till Hiddensee. Svensk kartläggning under 1600-talet". Av Ulla Ehrensvärd.
Engelsk kartförläggare under början av 1700-talet. - Se MOUNT & PAGE.
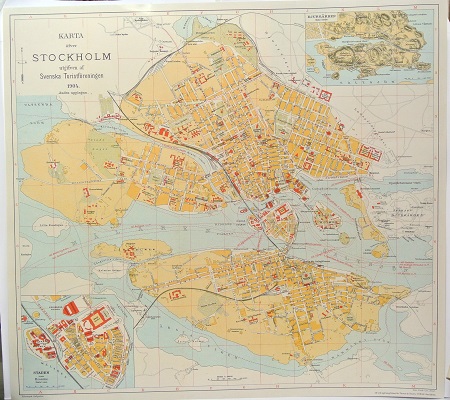
Karta öfver Stockholm. - 1904.
Murgröna, Hedera helix - Lindman, C. A. M, Bilder ur Nordens Flora 1917-26.
Cassini de Thury, César-François
Biografiska uppgifter:17 June 1714 – 4 September 1784
César-François Cassini de Thury (17 June 1714 – 4 September 1784), also called Cassini III or Cassini de Thury, was a French astronomer and cartographer.
Cassini de Thury was born in Thury-sous-Clermont (Oise), the second son of Jacques Cassini and Suzanne Françoise Charpentier de Charmois. He was a grandson of Giovanni Domenico Cassini, and would become the father of Jean-Dominique Cassini, Comte de Cassini.
In 1735, he became a member of the French Academy of Sciences as a supernumerary adjunct astronomer, in 1741 as an adjunct astronomer, and in 1745 as a full member astronomer.
In January, 1751 he was elected a Fellow of the Royal Society.
He succeeded to his father’s official position in 1756 and continued the hereditary surveying operations. In 1744, he began the construction of a great topographical map of France, one of the landmarks in the history of cartography. Completed by his son Jean-Dominique, Cassini IV and published by the Académie des Sciences from 1744 to 1793, its 180 plates are known as the Cassini map(fr).
The post of director of the Paris observatory was created for his benefit in 1771 when the establishment ceased to be a dependency of the French Academy of Sciences.
His chief works are: La méridienne de l’Observatoire Royal de Paris (1744), a correction of the Paris meridian; Description géométrique de la terre (1775); and Description géométrique de la France (1784), which was completed by his son ('Cassini IV').
César-François Cassini de Thury died of smallpox in Paris on 4 September 1784,
The Cassini projection is a map projection described by César-François Cassini de Thury in 1745. It is the transverse aspect of theequirectangular projection, in that the globe is first rotated so the central meridian becomes the 'equator', and then the normal equirectangular projection is applied.
In practice, the projection has always been applied to models of the earth as an ellipsoid, which greatly complicates the mathematical development but is suitable for surveying. Nevertheless the use of the Cassini projection has largely been superseded by the Transverse Mercator projection, at least with central mapping agencies.
Areas along the central meridian, and at right angles to it, are not distorted. Elsewhere, the distortion is largely in a north-south direction, and varies by the square of the distance from the central meridian. As such, the greater the longitudinal extent of the area, the worse the distortion becomes.
Due to this, the Cassini projection works best on long, narrow areas, and worst on wide areas.