1741-1810.
Gravör. Arbetade åt sin far, Tobias Conrad Lotter, och tog sedermera över dennes rörelse.
Död ca. 1568. Född i Piemonte.
Italiensk kartograf. Om hans liv finns inga säkra upplysningar förrän han 1544 dyker upp i Venedig som en fullt erfaren kartograf. Hans första kända arbete är en specialkarta över Spanien och Sicilien. 1548 gav han ut en Ptolemaeus-geografi med 60 kartor, varav 34 efter hans egna teckningar. Dessa kartor användes senare i flera andra utgåvor. Började i republiken Venedigs tjänst som kosmograf. 1550 dekorerade han stadshusets stora sal med en gigantisk Afrika-karta målad direkt på väggen. I övrigt utförde han under dessa år flera stora kartarbeten, både hela världskartor och specialkartor över mindre områden, i synnerhet Italien, södra Europa och övriga Medelhavsländer. Blev berömd och 1558 vald till professor i geografi vid 'Accademia della Fama'. Åt Venedig utförde han också olika målnings- och ingenjörsarbeten.
Bagrow.
Keere, Pieter van den [Kaerius, Petrus]
1571-c. 1646.
Pieter van den Keere was one of a number of refugees who fled from religious persecution in the Low Countries between the years 1570 and 1 590. He moved to London in 1584 with his sister who married Jodocus Hondius, also a refugee there, and through Hondius he undoubtedly learned his skills as an engraver and cartographer. In the course of a long working life he engraved a large number of individual maps for prominent cartographers of the day but he also produced an Atlas of the Netherlands (1617-22) and county maps of the British Isles which have become known as Miniature Speeds, a misnomer which calls for some explanation.
In about 1599 he engraved plates for 44 maps of the English and Welsh counties, the regions of Scotland and the Irish provinces. The English maps were based on Saxton, the Scottish on Ortelius and the Irish on the famous map by Boazio. These maps were not published at once in book form but there is evidence which suggests a date of issue (in Amsterdam) between 1605 and 1610 although at...
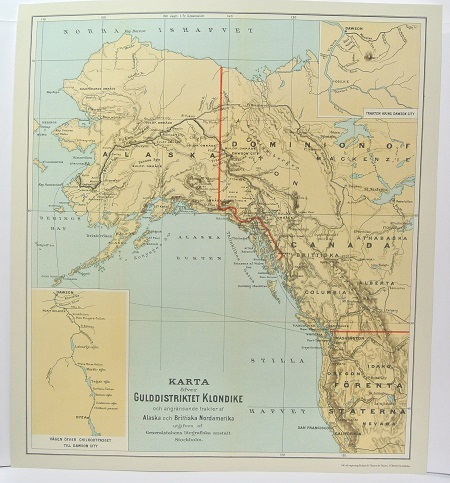
Gulddistriktet Klondike - ca 1897.
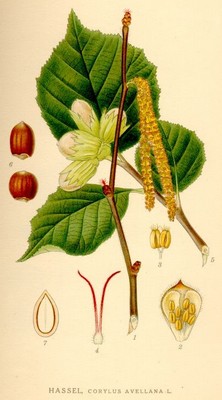
Hassel, Corylus avellana - Lindman, C. A. M, Bilder ur Nordens Flora 1917-26.
d'Anville, Jean Baptiste Bourguignon
Biografiska uppgifter:Born in Paris July 11, 1697 – died January 28, 1782.
Jean Baptiste Bourguignon d'Anville (born in Paris July 11, 1697 – January 28, 1782), was both a geographer and cartographer who greatly improved the standards of map-making. His maps of ancient geography, characterized by careful, accurate work and based largely on original research, are especially valuable. He left unknown areas of continents blank and noted doubtful information as such; compared to the lavish maps of his predecessors, his maps looked empty.
Work
D'Anville's map of China and Central Asia (1734) for du Halde's 'Description geographique de la Chine', compiled based on the first systematic geographic survey of the entire Chinese Empire by a team of French Jesuits (ca. 1700)
His passion for geographical research displayed itself from early years: at age of twelve he was already amusing himself by drawing maps for Latin authors. Later, his friendship with the antiquarian, Abbé Longuerue, greatly aided his studies.
His first serious map, that of Ancient Greece, was published when he was fifteen. At the age of twenty-two, he was appointed one the king's geographers, and began to attract the attention of first authorities. D'Anville's studies embraced everything of geographical nature in the world's literature, as far as he could muster it: for this purpose, he not only searched ancient and modern historians, travelers and narrators of every description, but also poets, orators and philosophers. One of his cherished subjects was to reform geography by putting an end to the blind copying of older maps, by testing the commonly accepted positions of places through a rigorous examination of all the descriptive authority, and by excluding from cartography every name inadequately supported. Vast spaces, which had before been bordered with countries and cities, were thus suddenly reduced mostly to a blank.
D'Anville was at first employed in the humbler task of illustrating by maps the works of different travellers, such as Marchais, Charlevoix, Labat and du Halde. For the history of China by the last-named writer he was employed to make an atlas, which was published separately at the Hague in 1737.[citation needed] Information for the maps of China came from land surveys made by the Chinese empire in 1708. His China maps have been called the 'standard Western source for the geography of China and adjacent regions,' throughout the 19th century.
In 1735 and 1736 brought out two treatises on the figure of the earth; but these attempts to solve geometrical problems by literary material were, to a great extent, refuted by Maupertuis' measurements of a degree within the polar circle. D'Anville's historical method was more successful in his 1743 map of Italy, which first indicated numerous errors in the mapping of that country and was accompanied by a valuable mémoir (a novelty in such work), showing in full the sources of the design. A trigonometrical survey which Benedict XIV soon after had made in the papal states strikingly confirmed the French geographer's results. In his later years d'Anville did yeoman service for ancient and medieval geography, accomplishing something like a revolution in the former; mapping afresh all the chief countries of the pre-Christian civilizations (especially Egypt), and by his Mémoire et abrégé de géographie ancienne et générale and his États formés en Europe après la chute de l'empire romain en occident (1771) rendering his labours still more generally useful. His last employment consisted in arranging his collection of maps, plans and geographical materials. It was the most extensive in Europe, and had been purchased by the king, who, however, left him the use of it during his life. This task performed, he sank into a total imbecility both of mind and body, which continued for two years, till his death in January 1782.
Honors
In 1754, at the age of fifty-seven, he became a member of the Académie des Inscriptions et Belles Lettres, whose transactions he enriched with many papers. In 1775 he received the only place in the Académie des Sciences which is allotted to geography; and in the same year he was appointed, without solicitation, first geographer to the king.
The crater Anville on the Moon is named after him, as was the community of Danville, Vermont.
Bibliography
D'Anville's published memoirs and dissertations amounted to 78, and his maps to 211. A complete edition of his works was announced in 1806 by de Manne in 6 vols. quarto, but only two had appeared when the editor died in 1832. See Bon-Joseph Dacier, Éloge de d'Anville (Paris, 1802). Besides the separate works noticed above, d'Anville's maps executed for Rollin's Histoire ancienne and Histoire romaine, and his Traité des mesures anciennes et modernes (1769), deserve special notice.
Bland arbeten:
Pere J. B. du Halde with maps by d'Anville, 'Description geographique de la Chine', 1735.
'Nouvel Atlas de la Chine', 1737.
'Atlas Generale', circa 1740.
'Geographie Ancienne et Abregee', 1769.
- Se bild.