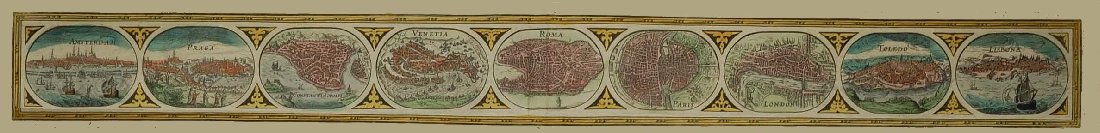
Född 1771 i Mézières, död 1850.
Lantmätare', kartograf och officer. Pierre Lapie gjorde i huvudsak en militär karriär, 1794 blev han geograf hos ingenjörstrupperna. Deltog i flera kampanjer och befodrades stegvis tills han blev överste i generalstaben. 1814 blev han chef för topografiska avdelningen på krigsministeriet. Hans kanske största uppdrag fick han dock 1818 när han skulle leda utförandet av de nya kartorna över Frankrike. Pierre Lapie kunde titulera sig kungens geograf i två omgångar, samt kejserlig geograf däremellan. Under sin tjänstgöringstid så låg han vid ett av gardesregementena. Hans son Alexandre Emile Lapie tjänstgjorde vid samma regemente. Fader och son samarbetade även som kartografer, bland annat med 'Atlas Universel de Geographie Ancienne et Moderne' Paris 1838.
Bland arbeten.
Atlas Universel de Geographie Ancienne et Moderne.
Död i juni 1598.
Emery Molyneux was an English Elizabethan maker of globes, mathematical instruments and ordnance. His terrestrial and celestial globes, first published in 1592, were the first to be made in England and the first to be made by an Englishman.
Molyneux was known as a mathematician and maker of mathematical instruments such as compasses and hourglasses. He became acquainted with many prominent men of the day, including the writer Richard Hakluyt and the mathematicians Robert Hues and Edward Wright. He also knew the explorers Thomas Cavendish, Francis Drake, Walter Raleigh and John Davis. Davis probably introduced Molyneux to his own patron, the London merchant William Sanderson, who largely financed the construction of the globes. When completed, the globes were presented to Elizabeth I. Larger globes were acquired by royalty, noblemen and academic institutions, while smaller ones were purchased as practical navigation aids for sailors and students. The globes were the first to be made in such a way that they ...
Bland arbeten.
'The Globes Celestial and Terrestrial Set Forth in Plano'
1762-1828.
Surveyor in Västergötland Province.
Sveriges sjökartor – A. Hedin.
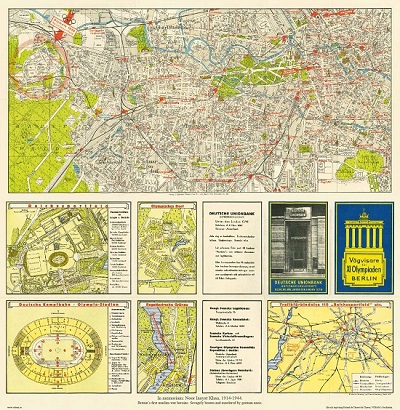
Vägvisare för XI Olympiaden i Berlin - 1936
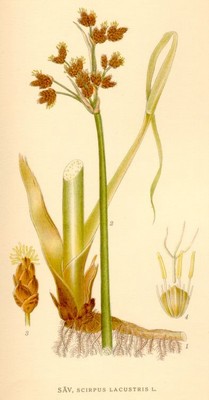
Säv, Scirpus lacustris - Lindman, C. A. M, Bilder ur Nordens Flora 1917-26.
Cassini de Thury, César-François
Biografiska uppgifter:17 June 1714 – 4 September 1784
César-François Cassini de Thury (17 June 1714 – 4 September 1784), also called Cassini III or Cassini de Thury, was a French astronomer and cartographer.
Cassini de Thury was born in Thury-sous-Clermont (Oise), the second son of Jacques Cassini and Suzanne Françoise Charpentier de Charmois. He was a grandson of Giovanni Domenico Cassini, and would become the father of Jean-Dominique Cassini, Comte de Cassini.
In 1735, he became a member of the French Academy of Sciences as a supernumerary adjunct astronomer, in 1741 as an adjunct astronomer, and in 1745 as a full member astronomer.
In January, 1751 he was elected a Fellow of the Royal Society.
He succeeded to his father’s official position in 1756 and continued the hereditary surveying operations. In 1744, he began the construction of a great topographical map of France, one of the landmarks in the history of cartography. Completed by his son Jean-Dominique, Cassini IV and published by the Académie des Sciences from 1744 to 1793, its 180 plates are known as the Cassini map(fr).
The post of director of the Paris observatory was created for his benefit in 1771 when the establishment ceased to be a dependency of the French Academy of Sciences.
His chief works are: La méridienne de l’Observatoire Royal de Paris (1744), a correction of the Paris meridian; Description géométrique de la terre (1775); and Description géométrique de la France (1784), which was completed by his son ('Cassini IV').
César-François Cassini de Thury died of smallpox in Paris on 4 September 1784,
The Cassini projection is a map projection described by César-François Cassini de Thury in 1745. It is the transverse aspect of theequirectangular projection, in that the globe is first rotated so the central meridian becomes the 'equator', and then the normal equirectangular projection is applied.
In practice, the projection has always been applied to models of the earth as an ellipsoid, which greatly complicates the mathematical development but is suitable for surveying. Nevertheless the use of the Cassini projection has largely been superseded by the Transverse Mercator projection, at least with central mapping agencies.
Areas along the central meridian, and at right angles to it, are not distorted. Elsewhere, the distortion is largely in a north-south direction, and varies by the square of the distance from the central meridian. As such, the greater the longitudinal extent of the area, the worse the distortion becomes.
Due to this, the Cassini projection works best on long, narrow areas, and worst on wide areas.