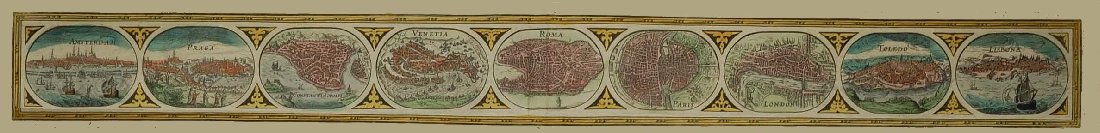
1733-1806. Born in Norrköping.
Dansk geograf, gav 1769 ut en geografisk karta över Medelpad.
Land Survey Apprentice 1749, commission surveyor for the Västernorrland region in 1757. Staff surveyor 1784 for Vasa county. Retired 1802.
Bland arbeten.
Karta över Medelpad.
Sveriges sjökartor – A. Hedin.
1757-1824.
Kartograf och kartförläggare.
Bland arbeten.
Kriegsschauplatz oder Graenzkarte zwischen Deutschland u. Franckreich... ca 1795.
Family of Dutch cartographers and globemakers.
Tooley
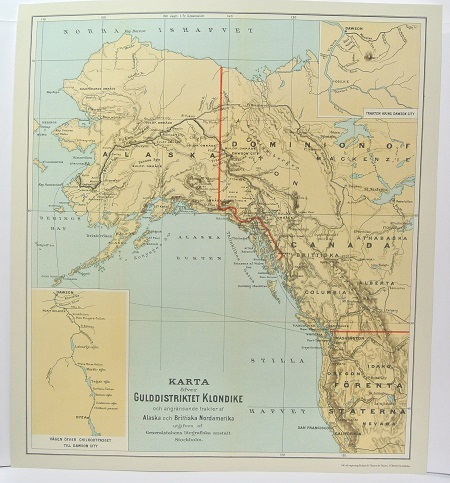
Gulddistriktet Klondike - ca 1897.
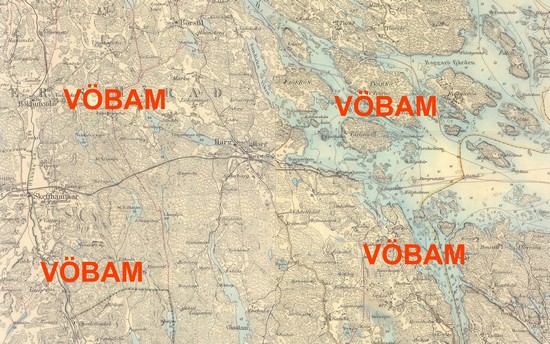
Harg - Östhammar. - 1878-1880.
MERCATOR, GERARD (Gerard de Cremere el. Kremer).
Biografiska uppgifter:5/3 1512- 2/12 1594. Född i Rupelmonde i Flandern, död i Duisburg.
Belgisk-tysk geograf. Från 1530 studerade han vid universitetet i Leuven under astronomen och kartografen Gemma-Frisius (se denne), och var dennes assistent under arbetet med hans jordglob. Hans första självständiga arbete, en Palestinakarta från 1537, finns det idag bara en känd kopia av. Lika sällsynta är flera av hans andra tidigaste arbeten. År 1541 konstruerade han en jordglob över jordklotet och en himmelsglob, båda på uppdrag av kejsare Karl V. År 1552 slog han sig ned i Duisburg där han sedan fortsatte sin verksamhet. 1569 gav han ut en liten bok om kronologi och samma år kom hans framstående världskarta. 1578 gav han ut Ptolemaeus geografi, kompletterad med sina egna kartor. Detta verk kom i 7 nyutgåvor, den senaste 1794. Mercator är ansedd som den mest betydelsefulla geografen sedan Ptolemaeus. Hans främsta verk, 'Atlas, sive cosmographicae meditationes de fabrica mundi' utkom första gången 1585 och slutfördes 1595, en kort tid efter hans död. Detta arbete var epokavgörande och kom fram till 1642 ut i 47 nyutgåvor med text på 6 olika språk. Under sina sista levnadsår hade Mercator goda medhjälpare i sina söner Rumold Mercator (se denne) och Arnold Mercator (se denne), samt tre av sina sonsöner. Ingen av dessa förde emellertid hans verk vidare. 1604 såldes företaget till Jodocus Hondius. På grund av den stora efterfrågan på Mercators atlas gav Jocodus Hondius ut en förminskad utgåva, 'Atlas minor' (1607) som även den fick stor utbredning under en lång rad år. Som kartograf tog Mercator i bruk en ny, cylindrisk kartprojektion som visade sig vara särskilt användbar för sjökort, och användes under flera århundraden.
For nearly sixty years, during the most important and exciting period in the story of modern map making, Gerard Mercator was the supreme cartographer, his name, second only to Ptolemy, synonymous with the form of map projection still in use today. Although not the inventor of this type of projection he was the first to apply it to navigational charts in such a form that compass bearings could be plotted on charts in straight lines, thereby providing seamen with a solution to an age-old problem of navigation at sea. His influence transformed land surveying and his researches and calculations led him to break away from Ptolemy's conception of the size and outline of the Continents, drastically reducing the longitudinal length of Europe and Asia and altering the shape of the Old World as visualized in the early sixteenth century.
Mercator was born in Rupelmonde in Flanders and studied in Louvain under Gemma Frisius, Dutch writer, astronomer and mathematician. He established himself there as a cartographer and instrument and globe maker, and when he was twenty-five drew and engraved his first map (of Palestine) and went on to produce a map of Flanders (1540) supervising the surveying and completing the drafting and engraving himself. The excellence of his work brought him the patronage of Charles V for whom he constructed a globe, but in spite of his favor with the Emperor he was caught up in the persecution of Lutheran protestants and charged with heresy, fortunately without serious consequences. No doubt the fear of further persecution influenced his move in 1552 to Duisburg, where he continued the production of maps, globes and instruments culminating in large-scale maps of Europe (1554), the British Isles (1564) and the famous World Map on 18 sheets drawn to his new projection (1569). All these early maps are exceedingly rare, some being known by only one copy.
In later life he devoted himself to his edition of the maps in Ptolemy's Geographia, reproduced in his own engraving as nearly as possible in their original form, and to the preparation of his 3-volume collection of maps to which, for the first time, the word 'Atlas' was applied. The word was chosen, he wrote, 'to honour the Titan, Atlas, King of Mauritania, a learned philosopher, mathematiciar, and astronomer' . The first two parts of the Atlas were published in 1585 and 1589 and the third, with the first two making a complete edition, in 1595 the year after Mercator's death.
Mercator's sons and grandsons, named above, were all cartographers and made their contributions in various ways to the great atlas. Rumold, in particular, was responsible for the complete edition in 1595. After a second complete edition in 1602, the map plates were bought in 1604 by Jodocus Hondius who, with his sons, Jodocus II and Henricus, published enlarged editions which dominated the map market for the following twenty to thirty years.
Bland arbeten:
Atlas, sive cosmographicae meditationes de fabrica mundi.
((Averdunk. - Bagrow. - Nederl. biogr. X.) ) - Se bild.