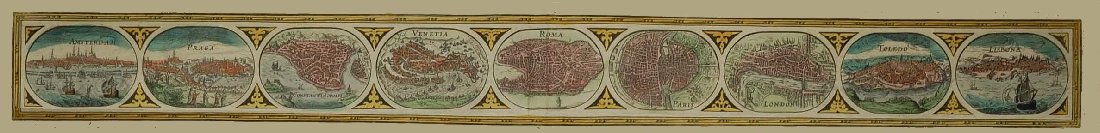
Bland arbeten.
Encyclopédie ou dictionnaire universel raisonné des connaissances humaines.
Bland arbeten.
Encyclopédie ou dictionnaire universel raisonné des connaissances humaines.
Död 1597.
Holländsk sjöfarare som ledde flera expeditioner för att finna en nordlig sjöförbindelse med Kina (Nordostpassagen). Sommaren 1594 nådde han Novaja Semljas västkust och följde denna norrut till 77:e breddgraden. Ett annat skepp i expeditionen seglade genom Vaigatsjstredet och hittade isfritt hav vidare längs nordkusten av Asien. En ny expedition året efter hittade emellertid denna passage blockerad av packis och tvingades vända. På sin tredje expedition 1596 hittade Barents Björnön och upptäckte Svalbard som inte tidigare varit känt sedan vikingarnas resor dit. Från Svalbard fortsatte han till Novaja Semlja och seglade runt nordspetsen av ön, där expeditionen blev den första att övervintra i Norra Ishavet. Då skeppen följande vår inte kom loss från isen tvingades manskapet överge dessa och färdas vidare i öppna båtar. Efter stora ansträngningar nådde de flesta fram till Lappland där de blev räddade, men Barents själv och flera andra omkom under resan.
Barentsz was a noted pilot who was convinced by t...
Salmonsen.
Vägvisare för XI Olympiaden i Berlin - 1936
Rast, Lycopsis Arvensis L. - Lindman, C. A. M, Bilder ur Nordens Flora 1917-26.

Biografiska uppgifter:Baptized October 7, 1586 in Haarlem, died 1643.
Dutch cartographer and traveller to Moscow.
Isaac Abrahamszoon Massa was a Dutch grain trader, traveller and diplomat, the envoy to Muscovy, author of memoirs witnessing the Time of Troubles and the maps of Eastern Europe and Siberia. Massa's experience in and knowledge of Muscovy transformed him into a Dutch 'Kremlinologist.' The Isaac Massa Foundation in Groningen aims to stimulate scientific and cultural contacts between the Russian Federation and the Netherlands.
Isaac Massa was born in a wealthy silk merchant's family that relocated from Liege to Haarlem before his birth. His ancestors could have been Italian huguenots who fled their homeland in the beginning of the Reformation. The family surname was also known as Massart, Massaert.
In 1601 Isaac left Haarlem for Moscow to assist the family trade. Isaac has been witness to the second half of Boris Godunov's reign that evolved into a civil war now known as the Time of Troubles. He survived the capture of Moscow by False Dmitriy I and left Russia in 1609, before the fall of tsar Vasily Shuysky. Massa compiled an account of 1601-1609 events (Dutch: Een cort Verhael van Begin en Oorspronk deser tegenwoordighe Oorloogen en troeblen in Moscovia totten jare 1610) presented to Stadtholder Maurice and reproduced in print in the 19th century.[3] In 1612-1613 Massa published two articles on Russian events and the geography of the Land of Samoyeds, accompanied with a map of Russia, in an almanac edited by Hessel Gerritsz. His notes on his various travels have been published in conjunction with maps by Henry Hudson.
These articles were translated and reproduced in European languages anonymously, because the author's name was removed in early Dutch reissues. The most complete translations were issued in Russian in 1937 (reissued in 1997) and in English in 1982. Massa's writing was based on an underlying concept of indispensable punishment for sins. Godunov, False Dimitri and the nation itself all paid for their mortal sins (Massa was confident that Godunov killed Feodor I and the real Tsarevich Dimitri). Russian sources consider him the least biased of contemporary Western witnesses, and a very well informed one (his comtemporary, Jacob De la Gardie, characterized Massa as 'extremely artful in learning other people's secrets').
Massa is credited with five published maps of Russia and its provinces, the last ones compiled around 1633, and two maps of Moscow city, including the schematic account of 1606 battle between Vasily Shuysky and Ivan Bolotnikov's armies. Retrieving original muscovite maps could have been dangerous for Massa himself and fatal for his Russian sources. Massa's rendition of the Siberian coast represented an advance in geography and for decades remained the only map of this region. It was subsequently copied by Mercator and Hondius, Jan Janssonius and Willem Blaeu.
In 1614 Massa returned to Moscow, this time accompanied by his brothers, as an envoy of States-General of the Netherlands to obtain an exclusive trade agreement similar to the recent Dutch-Ottoman treaty, as well as investigate the trade routes into Persia. Not only had the Dutch been keen to purchase grains but also persian silks. These had, equally so, been exported via Archangelsk. At the time Russian people showed great interest in artillery compounds such as lead and gunpowder. An average of 30 ships sailed each year to Archangelsk, a harbour near the White Sea - unfortunately during 1619 a fire broke out and destroyed the city completely, thereby ruining Massa's inventory. Additionally, upon his return Massa's ship encountered a heavy storm near Lapland.
In 1623/24 Massa was called upon by the Dutch Parliament (Staten-Generaal) to become an agent for Moscovia. However, his appointment proved to be a controversial one and drew serious opposition. He then made successful efforts to gain the interest of Gustaf II Adolf of Sweden to pursue trading grains with Russia. While nourishing the relationships between Russia and Sweden, he was knighted by the Swedish King in 1625 for his arduous efforts. One year later, in 1626, he attempted to gain exclusive rights on the trading of grains out of Russia.
Massa promoted the idea of setting up a trading cartel similar to the English Muscovy Company, but internal problems in the Netherlands delayed consolidation of traders into 1628. During his next voyage, in 1629, he travelled to Moscow to pave the way for his friend Elias Trip who by then had initiated a consortium. Massa indiscreetly advised Michael I of Russia and Michael's father, Filaret (the Patriarch of Moscow) of the internal affairs of the Dutch Republic. By doing so he attempted to tarnish the reputation of his competitors and personal opponents.
Because of the ongoing war between Sweden and Poland no grain could be exported through the city of Dantzig. One of his opponents, Klenck, himself a wealthy merchant trading in caviar, was given Russia's permission to export 10 or 12 cargo loads of rye meal. Meanwhile Trip feigned to act on behalf of the Swedish Monarchy.
In 1630 the price of grain remained extremely high due to increasing competition. Albert Burgh tried to ensure a monopoly for the City of Amsterdam. At the same time, countries such as Sweden and England endeavered to do the same. Russian merchants tried to curtail trading by limiting import and export exclusively via Archangelsk. For the next two decades Massa combined diplomatic service with his own business.
Massa has been the subject of two portraits by Frans Hals - solo (1626) and with his wife (1622); the latter is considered unique in composition for the period; the novel composition was probably Massa's own design. Massa owned a country house near Lisse, next to his brother-in-law, Adriaen Maertensz Block. He was the protector of Johannes Symonszoon van der Beeck, a painter from Haarlem.
Bland arbeten:
Plans of Moscow 1610, 1618;
N. Russia 1612 and
South Russia, used by Blaeu & Jansson.
(Tooley.) - Se bild.